South Asia Grapples with Devastating Monsoon Flooding
Hundreds Dead as Heavy Rains Lash Pakistan and India
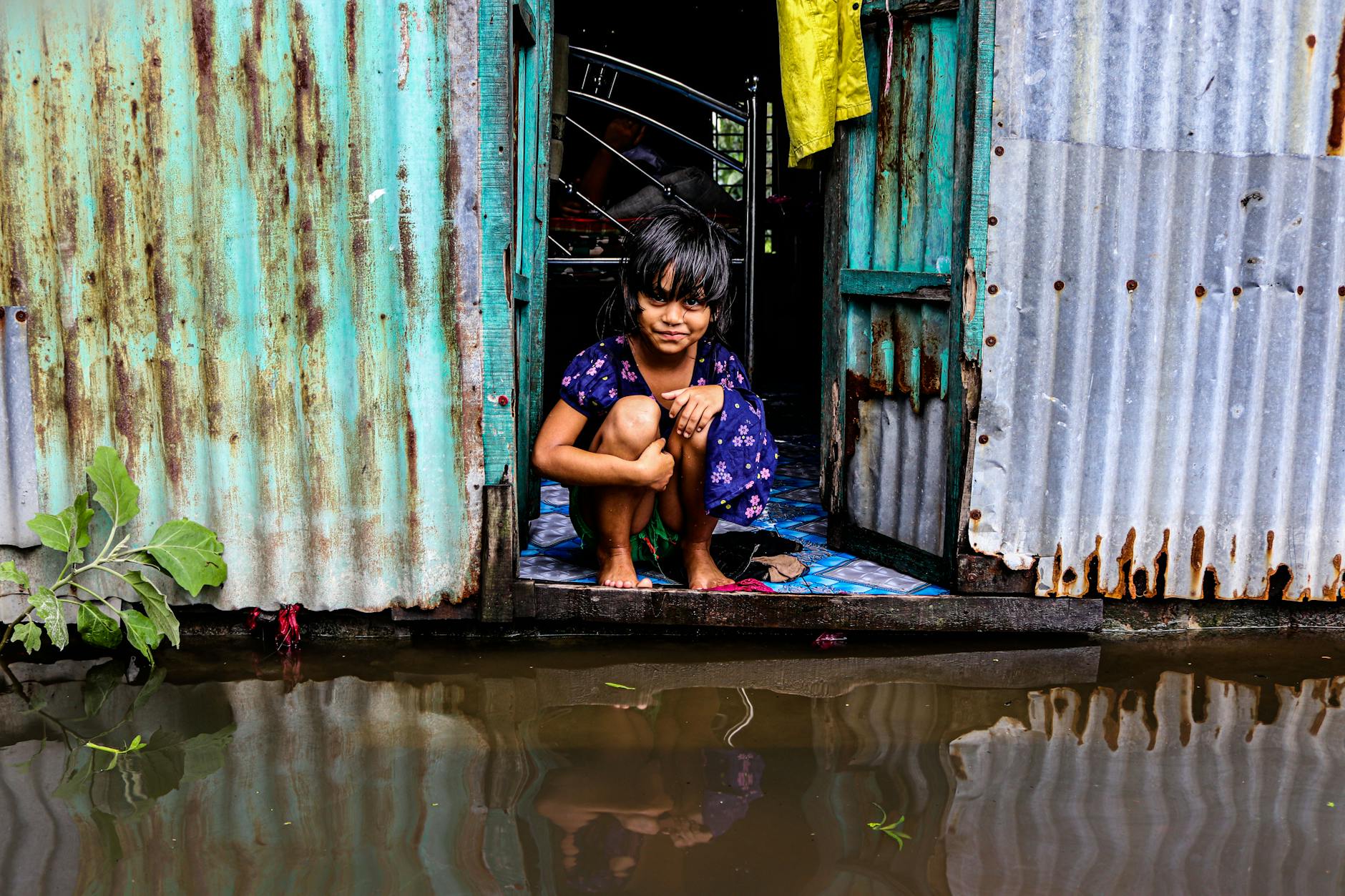
The Indian subcontinent is facing a severe monsoon season, with recent heavy rainfall triggering widespread flooding and landslides across Pakistan and parts of India. The downpours, described as some of the deadliest in recent years, have resulted in a significant loss of life and widespread destruction in mountainous regions and urban centers alike.
Understanding the Meteorological Factors
The current flooding event is attributed to a confluence of meteorological factors. According to weather tracking reports, moist air originating from the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea has been driven inland by strong southwesterly monsoon winds. This inflow of moisture, combined with developing low-pressure systems, has created conditions conducive to torrential downpours. These events have led to rapid water accumulation in river systems and overland flow, overwhelming natural and man-made drainage capacities.
Impacts on Pakistan and India
Pakistan has been particularly hard-hit, with reports indicating over 300 fatalities due to the relentless rains and subsequent flooding and landslides. The mountainous regions, often prone to such events during the monsoon, have experienced significant damage. In India, the city of Mumbai has also reported casualties, highlighting the vulnerability of densely populated urban areas to extreme weather. The monsoon season, typically a vital source of water for agriculture, has this year brought a level of devastation that is causing considerable concern among authorities and residents.
Broader Context of Monsoon Patterns
The monsoon system is a critical climatic feature for South Asia, providing the bulk of annual rainfall essential for agriculture and replenishing water resources. However, the intensity and timing of these monsoons can vary significantly year to year. Scientists study these variations to understand long-term climate trends and the potential impacts of climate change on regional weather patterns. While specific attribution of individual events to climate change requires detailed analysis, the increasing frequency or intensity of extreme weather events is a subject of ongoing scientific research and public discussion.
Challenges in Disaster Response and Preparedness
The scale of the flooding presents significant challenges for disaster response and recovery efforts. Rescuing stranded populations, providing shelter and essential supplies, and assessing the full extent of damage are immediate priorities for governments in the affected regions. The rebuilding process, including repairing infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and homes, will likely be a long and resource-intensive undertaking. Local authorities are often stretched thin during such widespread natural disasters, necessitating coordinated efforts and international aid.
Economic and Social Repercussions
Beyond the immediate human toll, the floods have substantial economic and social consequences. Disruption to transportation networks can impede the delivery of aid and essential goods. Damage to agricultural land and infrastructure can lead to food shortages and impact livelihoods. The displacement of communities also raises concerns about public health and access to basic services. The long-term economic recovery will depend on the extent of infrastructure damage and the resilience of local economies to withstand such shocks.
Looking Ahead: Relief Efforts and Future Preparedness
Relief organizations and government agencies are mobilizing to provide assistance to those affected by the floods. Efforts are underway to deliver food, water, and medical aid to affected populations. The immediate focus remains on saving lives and mitigating further suffering. In the longer term, discussions will likely turn towards enhancing disaster preparedness and resilience strategies. This may include improving early warning systems, strengthening infrastructure to withstand extreme weather, and implementing better land-use planning in flood-prone areas.
Key Takeaways
- Heavy monsoon rains have caused severe flooding and landslides in Pakistan and India.
- The events have resulted in hundreds of reported deaths and widespread destruction.
- Meteorological factors include the influx of moist air from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea, coupled with low-pressure systems.
- Disaster response and recovery efforts face significant challenges due to the scale of the flooding.
- The floods carry substantial economic and social repercussions, impacting infrastructure, livelihoods, and displaced communities.
- Focus is on immediate relief efforts and long-term strategies for disaster preparedness and resilience.
The situation remains dynamic, and affected populations are in urgent need of assistance. Further updates will be provided as more information becomes available from official sources.